Bosch 9.0 ESP
The Bosch 9 builds on the success of the Bosch 8: the software is modular, and a different variant is available for every application.
Bosch again claims less weight for the generation 9 unit, 30% lighter in fact, with the smallest variant now weighing just 1.1 kg. Other than that, the press releases do not say much about the technology in the ABS system. So we opened up a Bosch 9 Premium to satisfy our curiosity and were very surprised by what we saw: a green circuit board?!
We should probably explain why. Bosch has always used a very small ceramic circuit board cast onto an aluminium heat sink in their generation 5.3, 5.4, 5.7 and 8 units. This board was connected to the connector pins by small flexible connection wires. Since this method of making circuit boards is also widely used in other compact electronic devices and allows a very complex multi-layer architecture, we really expected competitor ATE Teves to switch to this approach at some point.
But ceramic circuit boards also have their drawbacks. Not only are the manufacturing costs a little higher, the flexible hybrid connections are also prone to failure in service. This may be the reason why Bosch decided to use the conventional design again.
We also have another theory: Bosch may have made this choice in order to standardise. You might not have noticed, but ATE Teves has used the same 47-pin connector since the MK25. They also added a universal 38-pin connector when the MK61 came out. Perhaps ‘by coincidence’, Bosch has also used a standard 38-pin connector and a 47-pin connector since generation 8. These ‘EuCon’ connectors have the same dimensions as the design used by ATE Teves, which means that a car manufacturer can still opt for ATE or Bosch relatively late in the design process. We strongly suspect that this choice has infl uenced Bosch’s thinking to some extent: Bosch's green circuit board is quite similar to the one used by competitor ATE.
Known complaints
- Various wheel sensor problems
- Various pump motor problems
- Various CAN and communication problems
- Speedometer no longer operates (no speed signal)
Can be remanufactured
| Item no. | Error code | Description |
| Various numbers | P0500 | Vehicle speed sensor malfunction |
| C1301 | Pressure sensor | |
| B12C9 | Vehicle speed signal incorrect |
Note: In case of error code P0500, please contact our customer service first.
Standard pin configuration Bosch 9 38-pin
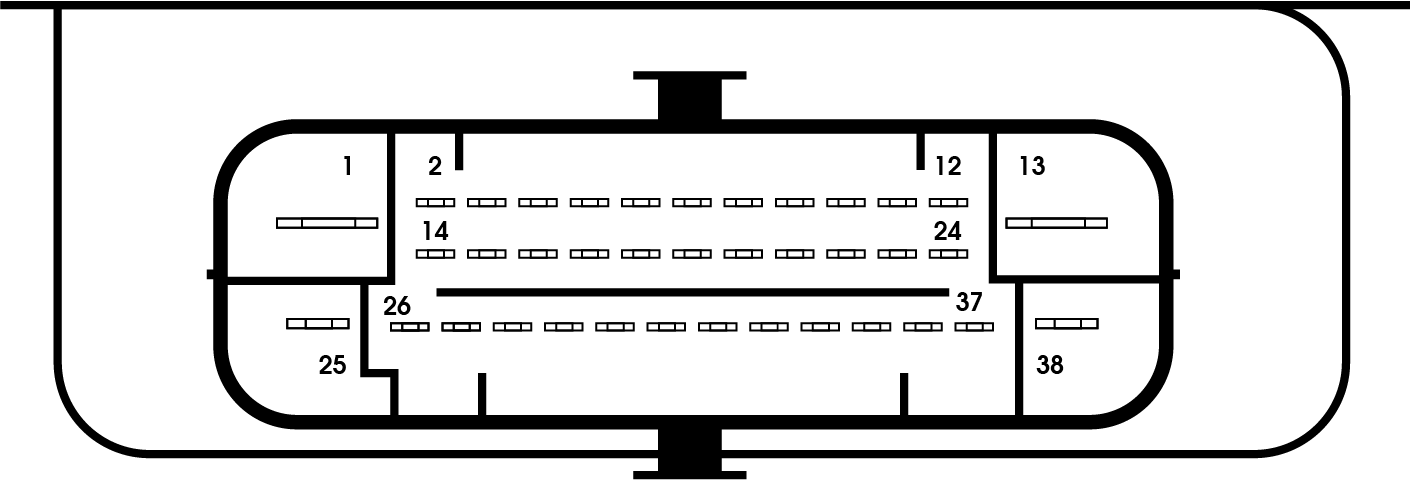
| Function | Pin |
| Ground | 13 |
| Ground | 38 |
| Power | 1 |
| Power | 25 |
| Ignition power supply | 28 |
| Wheel sensor FL | 8-19 |
| Wheel sensor FR | 4-16 |
| Wheel sensor RL | 18-31 |
| Wheel sensor RR | 17-29 |
| CAN L | 14 |
| CAN L2 | 15 |
| CAN H | 26 |
Bosch 9.0 ESP Wide
Bosch has rolled out different versions during the production of the Bosch 9 series. For example, there is a version without ESP functionality, but also a version with ESP functionality with a different pin configuration. This 46-pin version is also known as the Bosch 9.0 ESP Wide. This version has been used in the Audi A4, among other things, where error code C123EF0 is a frequently heard problem.
Standard pin configuration Bosch 9 46-pin
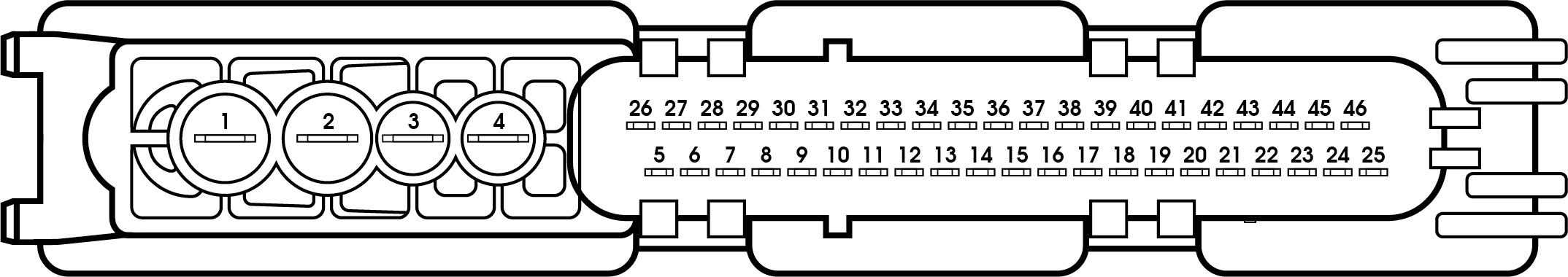
| Function | Pin |
| Ground | 14 |
| Ground | 46 |
| Power | 1 |
| Power | 30 |
| Ignition power supply | 31 |
| Wheel sensor FL | 22-37 |
| Wheel sensor FR | 23-39 |
| Wheel sensor RL | 21-26 |
| Wheel sensor RR | 7-24 |
| CAN L | 18-19 |
| CAN L2 | 25 |
| CAN H | 4-5 |
| CAN H2 | 11 |
Always use original wheel sensors when replacing parts!
When replacing wheel sensors, ACtronics recommends that you always choose the OEM product. These sensors should also be selected by chassis number or license plate, because many different types are available and they all look alike on the outside. Fitting the wrong wheel sensor can cause confusion for mechanics. The sensor will work in principle, but the signal differs from what the ECU expects to receive. The ECU will then usually generate error codes that relate to the wheel sensor's impedance.
Changing the brake fluid is extremely important!
We probably don’t need to explain that brake fluid is hygroscopic and naturally attracts moisture. Yet the damage that this moisture can cause is often underestimated. The moisture in the brake fluid will also get past the valves in the HCU and these valves will seize after a time (corrosion). ABS units with seized valves in the HCU are regularly sent to us for remanufacture.
Tips in the event of problems after removal of the HCU
- Only bleed the brake system according to the official procedure, i.e. with the help of diagnostic equipment.
- Always code/calibrate the pressure sensor again after an overhaul! Then check the live data: the brake pressure should be between -1 and 1 bar at rest. The pressure should increase when the pedal is pressed.
Dirt in, damage to and play in wheel bearings
In the event of wheel sensor problems, always check the wheel bearings for dirt, damage and play. The signal that the magnet ring or toothed ring is supposed to generate must fall within a narrow tolerance band, so even a small deviation can immediately cause a malfunction.

 da
da de
de es
es fr
fr it
it nb
nb nl
nl pt
pt sv
sv fi
fi